7 Surprising Side Effects of a Low-Fat Diet Worth Knowing
Have you ever wondered what the side effects of a low-fat diet could be? Worried that eating fat will make you gain weight? Turns out, there are consequences of a low-fat diet. Chelsey Amer, MS, RDN, CDN, investigates what happens when you don’t eat enough fat. Read up on low-fat diet side effects and why adding more of this necessary macronutrient may help you achieve your goals.
If the low-fat craze of the 1990s influenced your comfort around eating (or not eating) fat, you’re not alone. But let’s clarify: Eating fat doesn’t make you fat! It’s widely accepted that healthy fats are important for your well-being. Yet still, as a registered dietitian, I see clients every day who avoid fat due to fear of gaining weight.
Before we get to the low-fat diet side effects, let’s first look at the benefits of eating healthy fats and how much you should eat per day.
Benefits of Healthy Fats
To begin, there are many healthy high-fat foods you can include in your diet, such as:
- Olive oil
- Avocados
- Olives
- Nuts and seeds
- Fatty fish
Among other things, the benefits of healthy fats include:
- Support for heart health
- A stable mood
- Glowing skin
- Balanced hormones
- Proper vitamin absorption
Conversely, opting for low- and no-fat products—like zero-percent fat Greek yogurt or powdered peanut butter—means you’re missing out on the many health and beauty benefits of healthy fats. That said, not all fats are created equally.
How Much Fat Should You Eat Per Day?

The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) for fat is 20 to 35 percent of your daily calories.
However, according to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans, only 10 percent or less of that quota should come from saturated fat. Examples of saturated fat include fat from animals, full-fat dairy, and coconut oil. Unsaturated fat, on the other hand, is found in things like avocado, nuts and seeds, and fatty fish like salmon.
7 Low-Fat Diet Side Effects to Know
So what happens when you skip out on fat? There are several disadvantages of a low-fat diet. For starters, when you skip fat in your meals, it’s harder to:
- Feel satisfied with your meals
- Curb your cravings
- Stay full between meals and snacks
If you’re still wary of adding fats to your meals, the potential side effects of a low-fat diet may change your mind.
1. Flaky, Dry Skin
Did you know that fat is an important component of skin cell membranes?
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, you shed 30,000 to 40,000 old skin cells daily. Your body constantly makes new ones, and it must have enough fat to do so. This is especially significant because fat helps maintain the skin barrier, locking in moisture and protecting your skin from irritants.
However, it’s not enough to simply lather yourself in lotion from head to toe. You need to eat fat to nourish your skin cells from the inside out otherwise you run the risk of dealing with dry skin.
Specifically, consuming essential fatty acids—found in fatty fish, nuts, seeds, high-quality vegetable oils, and more—can help mitigate the inflammatory response in your skin, reducing redness.
Aim to consume fish twice weekly, as well as nuts, seeds, avocado, and olive oil for glowing moisturized skin.
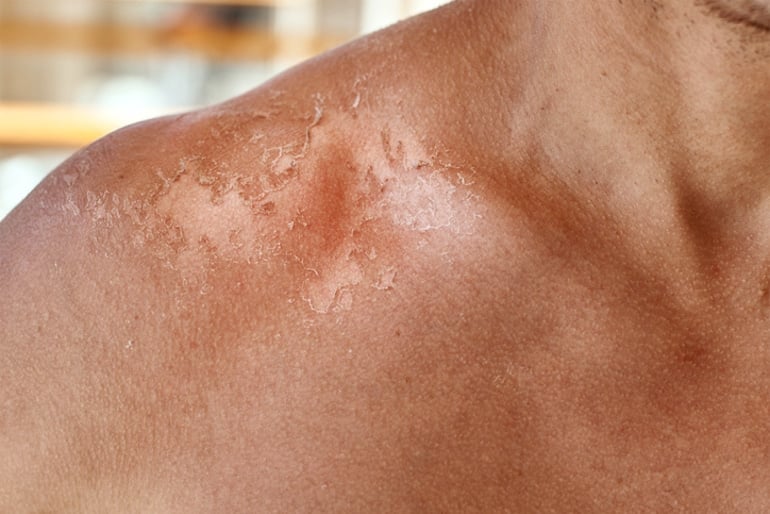
2. Increased Sensitivity to Sunburn
You’re likely aware that it’s important to apply sunscreen daily—especially when you’re outside. But did you know that what you eat impacts your ability to burn, too?
Researchers have found that essential fatty acids (like omega-3s) can help reduce cellular stress and inflammation caused by UV rays. So, if you’re not eating enough fat in your diet, you might be prone to more sunburn, which can lead to increased signs of aging and skin cancer.
Though we need more research on this point, you can start protecting your skin from within by adding omega-3-rich foods like fatty fish, nuts, and seeds to your shopping cart. And yes: Sunscreen is still necessary!
3. Mood Imbalances
Your brain is 60 percent fat, so it’s no wonder that potential side effects of a low-fat diet include brain fog and moodiness.
Studies consistently show that symptoms of low-fat intake include increased anger, irritability, and low mood due to changes in serotonin, a feel-good brain chemical. Furthermore, researchers found that women following a low-fat diet over an extended period of time reported greater levels of stress.
Essential fatty acids, like omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, are well-known to support mental health. On the other hand, low omega-3 fatty acid intake is associated with mood imbalances. That’s why healthy high-fat nuts, seeds, fatty fish, and even chocolate are often considered some of the best brain foods.
4. Hormone Imbalances
Many key hormones in your body are made from fat. For this reason, one of the low-fat diet dangers is interference with proper hormone production and function.
Plus, certain sex hormones—including estrogen and testosterone—rely on fat. This means that very low-fat diets can interfere with proper hormone balance, potentially leading to:
- Low libido
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Fertility issues
If you want to increase your overall intake, try this chocolate avocado mousse recipe for a delicious dose of healthy fats from avocado.
5. Constant Hunger
Feel hungry around the clock? You may want to switch up your diet to ensure you’re eating enough fat.
Out of the three major macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, and fat), fat digests the slowest. It takes longer to digest and absorb fat from your food, meaning you can endure longer stretches free from hunger pangs (and escape those late-night snacking habits). However, it’s not just fat’s slower rate of digestion that keeps your hunger at bay. Hormones also play a key role in satiety. Yet another benefit of healthy high-fat foods is that they help turn off ghrelin (aka the hunger hormone), so you get the message to pause your food intake.
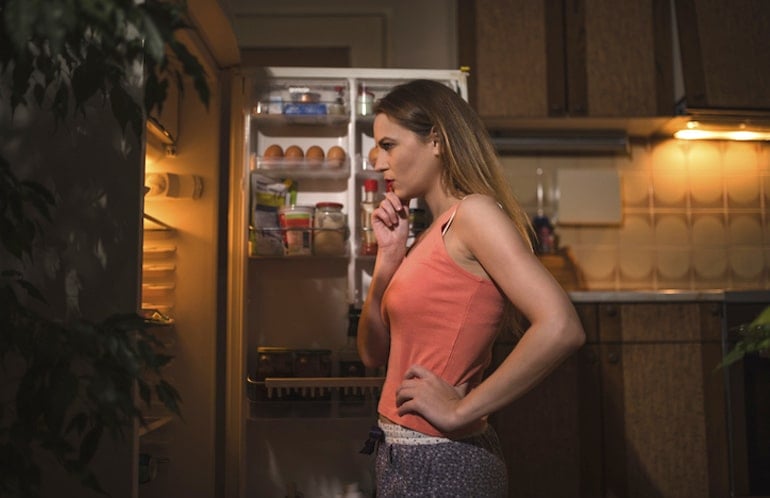
6. Poor Vitamin Absorption
Did you know that you actually *need* to eat fat to adequately absorb vitamins including A, D, E, and K?
For instance, eating vitamin K-rich dark leafy greens without any source of fat will lead to less vitamin K absorption than if you added healthy fats—like oil-based dressing or avocado—to the mix.
That’s because vitamins A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble vitamins, meaning they require fat for better absorption in your body.
7. More Cravings
Another negative low-fat diet side effect? Increased cravings. If you find yourself constantly grabbing highly processed, high-carb, and high-sugar foods, you’ll be better off boosting your fat intake throughout the day.
Choosing healthy high-fat foods (like full-fat dairy over fat-free versions) can lead to greater satisfaction from food and therefore fewer cravings. Plus, adding healthy fats to your meals will better balance your diet, thus curbing cravings.
Low-Fat Diet FAQs
- What is a low-fat diet?
A low-fat diet emphasizes reducing total fat intake, particularly saturated fats, while encouraging the consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins to promote overall health. - What are the benefits of a low-fat diet?
A low-fat diet can help lower cholesterol levels, reduce the risk of heart disease, and support weight loss efforts when combined with a balanced intake of nutrients. - Can you lose weight on a low-fat diet?
Yes, many people can lose weight on a low-fat diet by creating a calorie deficit while still meeting their nutritional needs through other food groups. - What foods are allowed on a low-fat diet?
Foods typically allowed on a low-fat diet include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, fish, low-fat dairy products, and legumes, while avoiding high-fat processed foods. - Are all fats bad in a low-fat diet?
Not all fats are bad; a low-fat diet should focus on reducing saturated and trans fats while allowing healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, and olive oil in moderation. - Who should follow a low-fat diet?
A low-fat diet may be beneficial for individuals looking to manage their weight, lower cholesterol levels, or improve heart health, but it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
The Takeaway
Not only can a lack of fat in your diet lead to unpleasant side effects, but it can also throw off your nutrient balance. Take care to follow a well-balanced diet that includes a moderate amount of fat so you can feel your best. Then, to go the extra mile and get personalized recommendations, it’s best to consult a dietitian.










